

This may be readily accomplished by the traditional technique of constructing lines in the plane.

This paper begins by showing how the terms of the stress matrix may be represented first vectorially and then graphically, giving examples of simple structures.īefore looking at stability, graphic statics is first employed in the initial equilibrium step, establishing the reciprocal diagrams of form and force. In the Guest description, it is the closely related stress matrix that plays this role, and that will be the primary study of this paper. This matrix decomposes into two components similar to the possibly more familiar decomposition of a stiffness matrix into a material part and a geometric part, with the latter representing the effects of forces on the overall system stiffness. Building on work of Pellegrino & Calladine and Connelly & Whiteley, Guest provides a matrix formulation of the exact tangent stiffness of any prestressed pin-jointed truss with respect to perturbations about its deformed equilibrium configuration. In this paper, we thus require a clear statement of structural behaviour which considers equilibrium at the deformed shape. While it would be tempting to describe these as higher-order effects, this is not strictly correct: the instability phenomena have been missed because the equilibrium equations were written at the undeformed shape. An analyst will need to create a considerably more sophisticated model in order to successfully simulate such stabilizing and destabilizing effects. While better theories can describe buckling and tension stiffening, the inability of traditional matrix formulations of structural mechanics to undergo such destabilization persists even into the large finite-element packages routinely used in structural analysis. Such tension stiffening and compression de-stiffening are not described by the simplest structural theories where equilibrium equations are written at the undeformed configuration. An axial compressive force would cause the system to buckle, while a tension force would tend to pull the structure straight, adding stiffness such that the structure would even be capable of carrying some transverse load.Ī bar with a central hinge pulls straight under tension but is unstable in compression and buckles laterally. Figure 1 shows a simple example where a pair of hinged bars has a mechanism involving lateral deflection. In this paper, the methodology is extended to quantify the stiffness that arises due to the presence of forces within the members, allowing the stability to be assessed. The case of interest is known as ‘prestress stability’ and it concerns structures which possess at least one mechanism which may be stabilized or destabilized by the geometric stiffness effects that arise from the axial forces carried by the structural members.įollowing Maxwell the graphic analysis of the equilibrium of a pin-jointed truss is accomplished via a pair of reciprocal diagrams, with the truss geometry given by the form diagram, while the force diagram represents an equilibrium set of axial forces within that truss. Here, we extend the methods to describe the stability of such structures. This method is advantageous when the axial forces in specific members are required in a truss with several members.ĥ.1 Classify the trusses shown in Figure P5.1a through Figure P5.1r.ĥ.2 Determine the force in each member of the trusses shown in Figure P5.2 through Figure P5.12 using the method of joint.ĥ.3 Using the method of section, determine the forces in the members marked X of the trusses shown in Figure P5.13 through Figure P5.19.Graphic statics has traditionally concerned itself with the equilibrium of pin-jointed trusses.
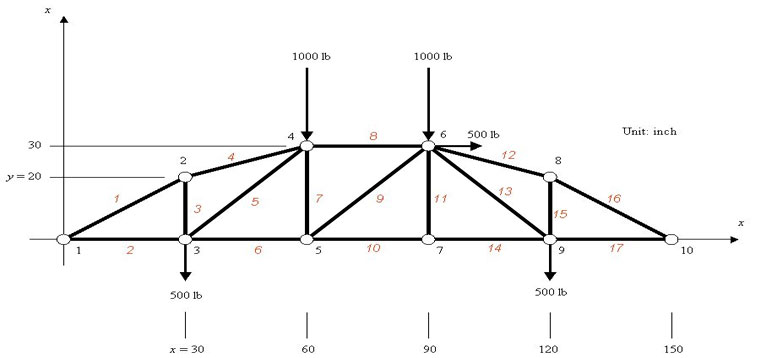
The member forces are determined by considering the equilibrium of the part of the truss on either side of the section.

Method of section: This method entails passing an imaginary section through the truss to divide it into two sections. Joints are isolated consecutively for analysis based on the principle that the number of the unknown member axial forces should never be more than two in the joint under consideration in a plane trust.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
